SOIL EROSION
WIND EROSION
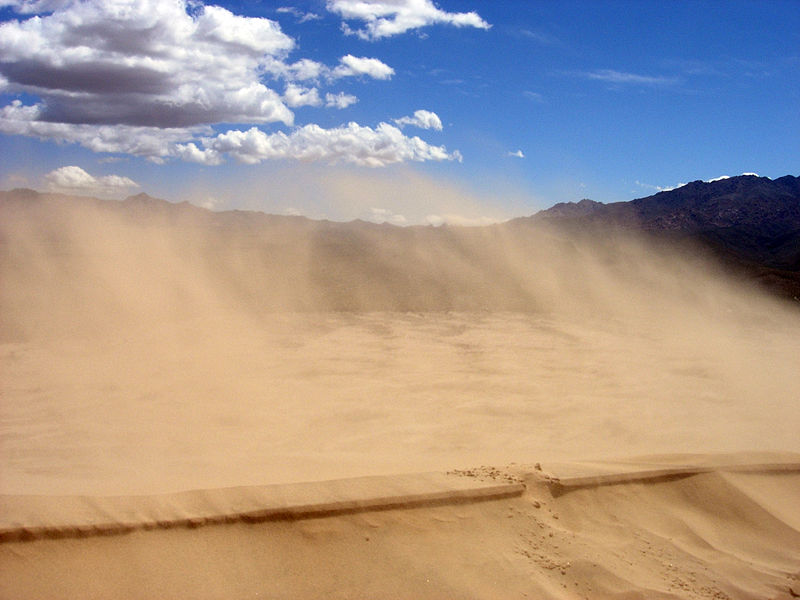
Wind erosion is the process by which wind carries and moves soil and other particles from one place to another. It is a natural process that occurs in areas with dry and arid climates, where there is little vegetation to stabilize the soil and where wind speeds are high. Wind erosion can have significant impacts on the environment, including the loss of topsoil, reduced soil fertility, and damage to infrastructure and property.

Saltation is a type of wind erosion that occurs when the wind lifts and moves small particles of soil and other materials, causing them to bounce along the ground. During saltation, the particles are lifted by the wind and then dropped back to the ground, where they collide with other particles and cause them to be lifted in turn. This bouncing action can cause soil particles to be lifted and moved significant distances, and can result in the loss of topsoil and reduced soil fertility.
Saltation can also have other impacts on the environment, such as the creation of sand dunes, the deposition of sediment in waterways, and the transport of pollutants over long distances. It can also cause damage to infrastructure and property, as the bouncing particles can erode surfaces and cause wear and tear on buildings and other structures.
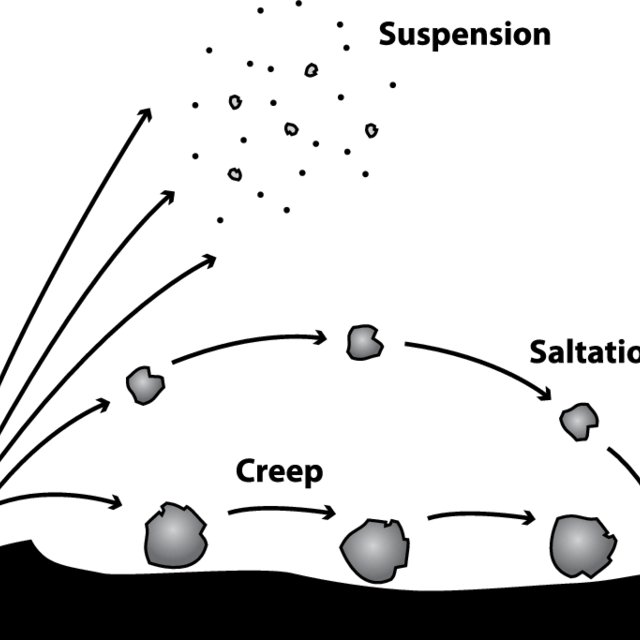
Suspension is a type of wind erosion that occurs when the wind lifts fine particles of soil and dust into the air, carrying them over long distances. During suspension, small particles are lifted by the wind and carried along in the air currents. These particles can travel great distances and can have a significant impact on the environment.
Suspension can have several impacts on the environment, such as reducing air quality and causing respiratory problems, depositing sediment in waterways, and reducing the fertility of soil by removing the nutrient-rich topsoil. It can also have economic impacts, such as damage to infrastructure, reduced visibility for transportation, and loss of agricultural productivity.
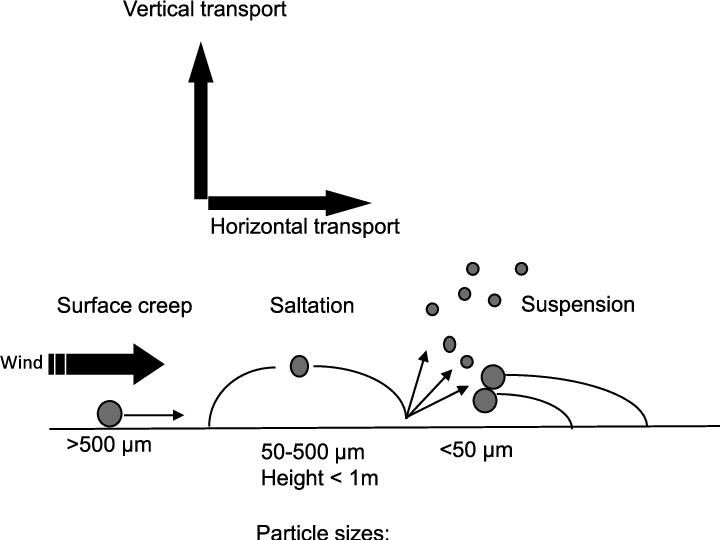
Surface creep is a type of wind erosion that occurs when the wind moves larger particles of soil and other materials along the ground. During surface creep, the wind exerts a force on the surface of the soil, causing it to move slowly along the ground. This type of erosion is most common in areas with loose or poorly compacted soil, such as sandy or loamy soils. Surface creep can have several impacts on the environment, such as the loss of topsoil, reduced soil fertility, and damage to infrastructure and property.


